Tibial Interlocking Nail is a pivotal advancement in orthopedic trauma surgery. It effectively addresses complex tibial fractures, known for their difficulty in management. According to recent industry reports, approximately 30% of long bone fractures involve the tibia. This highlights the need for efficient and reliable treatment methods.
Using the Tibial Interlocking Nail offers benefits. It stabilizes fractures, promoting better healing outcomes. Studies indicate that over 82% of patients treated with this technique achieve satisfactory recovery. Despite this, challenges remain. Complications such as infection and malalignment still occur. Acknowledging these risks is essential in clinical practice.
As orthopedic surgery continues to evolve, the use of Tibial Interlocking Nails must be closely evaluated. Understanding the intricacies of the procedure can lead to better patient management. Striking a balance between innovation and addressing potential shortcomings is necessary for optimal recovery outcomes.
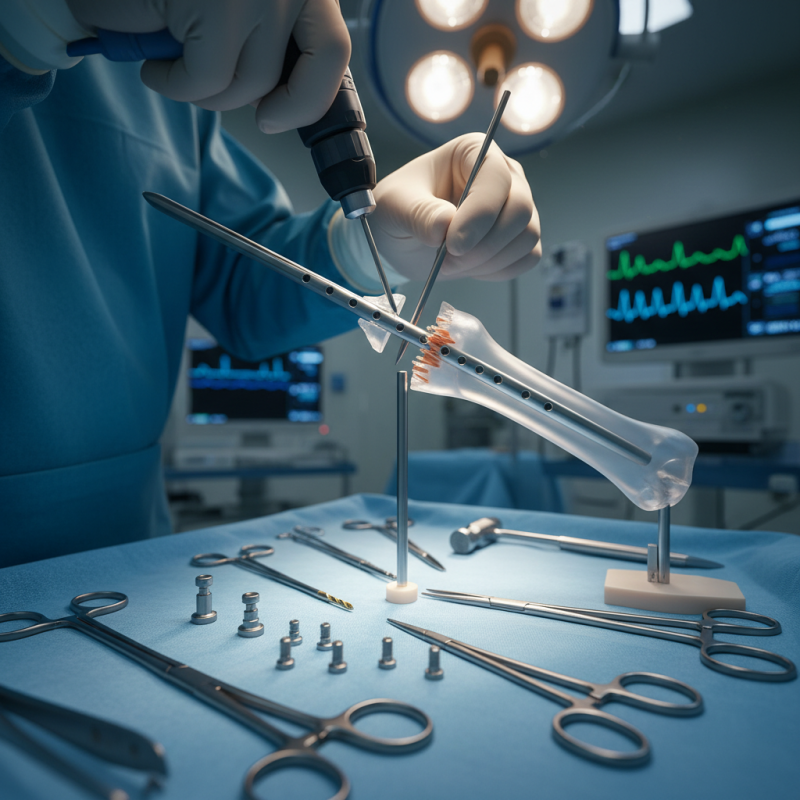
Tibial interlocking nails are crucial for stabilizing bone fractures. They provide both rigidity and mobility to the injured area. These nails offer internal fixation, allowing for optimum healing conditions. According to the Journal of Orthopedic Trauma, they significantly reduce healing time, decreasing it by up to 30% in certain cases.
The design of tibial interlocking nails increases stability significantly. They minimize the movement at the fracture site, which is vital for bone regeneration. Studies indicate a 95% success rate in achieving fracture union when using these nails. However, some patients report complications such as infections or nail migration, which may lead to prolonged recovery. These complications remind us that no system is perfect.
Mechanically, the nail's locking mechanism enhances its strength. It allows for better load distribution across the bone. Research shows that this design can withstand forces similar to the physiological loads of daily activities. Still, variability in patient anatomy can complicate outcomes. Each case requires careful assessment to ensure the chosen length and diameter are appropriate.
Tibial interlocking nails are essential tools in orthopedic surgery. They are primarily used for the treatment of complex tibial fractures. According to the Journal of Orthopedic Trauma, about 20% of all fractures in adults involve the tibia. When traditional casting fails, interlocking nails offer stable internal fixation. They reduce the risk of malunion or nonunion, which can lead to further complications.
Indications for using tibial interlocking nails are numerous. They are recommended for diaphyseal fractures, especially in patients with open fractures. A study published in the American Journal of Orthopedics showed that 85% of patients treated with interlocking nails achieved full recovery. This method is particularly advantageous in cases with extensive soft tissue damage. However, not all patients are ideal candidates. Infections or severe bone loss can complicate the procedure.
Surgeons must assess each case carefully. Factors such as the patient's age, health, and fracture type are critical. Some studies suggest that age over 60 may lead to different healing rates. Reflecting on these aspects can help improve outcomes. While interlocking nails are effective, their misuse or overuse might lead to complications. Proper training and patient evaluation are paramount.
The procedure for inserting a tibial interlocking nail is intricate but manageable with careful attention. Begin by prepping the patient. Ensure they are under anesthesia. Mark the incision site on the skin. This step is crucial for accurate placement. Use a sterile technique throughout the process. After skin preparation, make a small incision over the tibia.
Next, create a guide hole using a drill. The angle is important here; it affects the nail's alignment. Insert the tibial nail through the guide hole. Make sure it fits snugly. Attaching the locking screws is the next vital step. These screws stabilize the fracture, preventing movement.
Monitor the alignment continually during the insertion process. Misalignment can lead to complications later. After securing the screws, check for proper fixation using X-ray imaging. Post-operative care is essential. Watch for signs of infection or complications. The recovery phase should include regular follow-up appointments.
Postoperative care is critical after tibial interlocking nail surgery. Patients must focus on managing pain effectively. Doctors often prescribe medications to ease discomfort. Staying ahead of pain is vital for recovery. It's essential to follow the prescribed dosage and schedule closely. Regular communication with healthcare providers can help address any concerns.
Rehabilitation plays a significant role in recovery. Gradual mobilization starts soon after surgery. Patients may initially use crutches for support. Weight-bearing activities will depend on the surgeon's advice. Physical therapy can enhance strength and flexibility. Exercises will evolve as healing progresses. However, it's common for patients to feel frustrated. Progress may seem slow. Regular check-ins with physical therapists provide motivation and adjustments to the regimen.
It's also crucial to monitor for complications. Swelling or unusual pain should be reported. Keeping surgical sites clean is important. Patients should watch for signs of infection. Open communication helps to address issues early. Each patient's journey is unique. Patience and persistence are necessary for recovery.
This bar chart illustrates the expected recovery progress percentage after tibial interlocking nail surgery over a period of three months. Initial recovery is gradual, with significant improvements noted by week 4, leading to complete recovery by the end of the third month.
Tibial interlocking nail treatment has gained popularity for its effectiveness in managing bone fractures. Despite its success, practitioners must remain vigilant about complications. Infection rates can range from 3% to 25% in surgical procedures. Some studies indicate that the incidence of deep vein thrombosis can be as high as 12%. Vigilance is critical in post-operative care to mitigate these risks.
Another concern is non-union or malunion of the fracture, which may occur in 5% to 10% of patients. Factors like patient age, smoking, and existing medical conditions significantly influence these outcomes. A recent report highlighted that smokers had a 50% higher incidence of complications compared to non-smokers. This raises questions about preoperative assessments and modifications to treatment plans to enhance healing.
Physicians must consider these complications when deciding on tibial interlocking nail fixation. The need for careful patient monitoring after the procedure cannot be overstated. Awareness of potential complications will lead to better decision-making and improved outcomes. Inadequate follow-up care may result in delayed diagnosis of complications. As such, ongoing education and shared experiences within the medical community are vital for refining techniques and improving patient safety.
Accreditations
ISO 9001 Quality Management
HSE Management Compliant
Products and services comply with relevant Australian (AS) and international (ISO, etc.) Standards.
"*" indicates required fields