In the ever-evolving landscape of industrial applications, selecting the right actuated ball valve is crucial for ensuring optimal performance, efficiency, and reliability. This critical component plays a significant role in controlling the flow of fluids within various systems, making its selection pivotal for operational success. With numerous options available on the market, it can be challenging to determine which actuated ball valve best suits your specific needs.
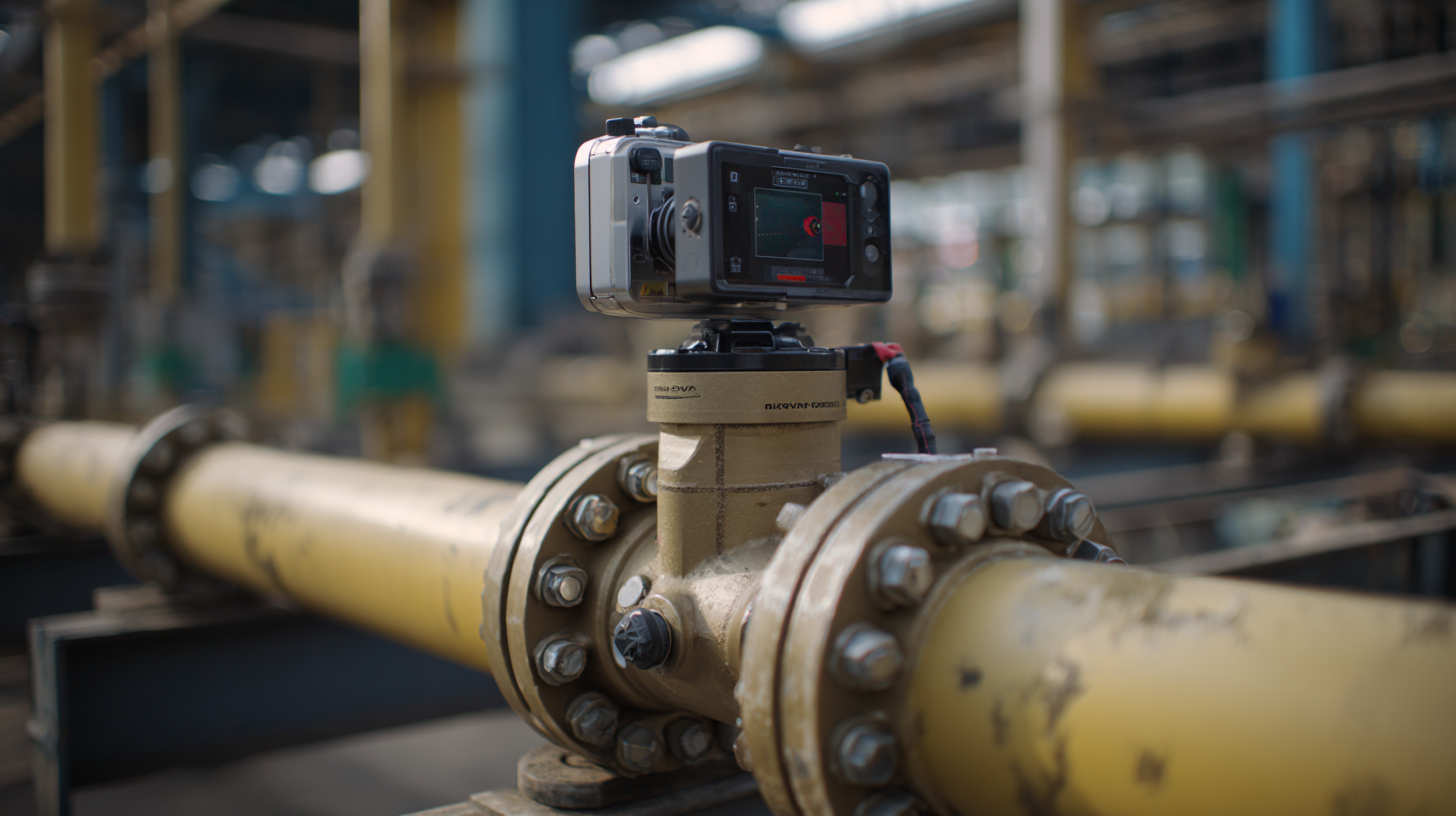

Factors such as size, pressure rating, material compatibility, and actuator type must be evaluated to make an informed decision. In this blog, we will explore the key considerations and best practices for choosing the perfect actuated ball valve for your industrial application, ensuring that you make a choice that maximizes efficiency and minimizes downtime in your operations.
Actuated ball valves play a crucial role in industrial applications, offering precise control over the flow of liquids and gases. Understanding the basics of these valves is essential for making informed decisions. At their core, actuated ball valves feature a spherical disc that controls flow by rotating 90 degrees. This simple yet effective design allows for quick opening and closing, which is vital in processes that require rapid response times. The integration of actuators—either electric, pneumatic, or hydraulic—further enhances their functionality, enabling automated operations and reducing the need for manual intervention.
In industrial settings, the choice of actuated ball valve is influenced by various factors, including the medium being transported, pressure ratings, and temperature conditions. Compatibility with the existing piping system is also critical to ensure optimal performance. Moreover, factors such as the valve's size, material composition, and actuator type can significantly impact overall efficiency and maintenance needs. By thoroughly understanding these aspects, industries can select the right actuated ball valve that not only meets operational requirements but also enhances reliability and safety in their processes.
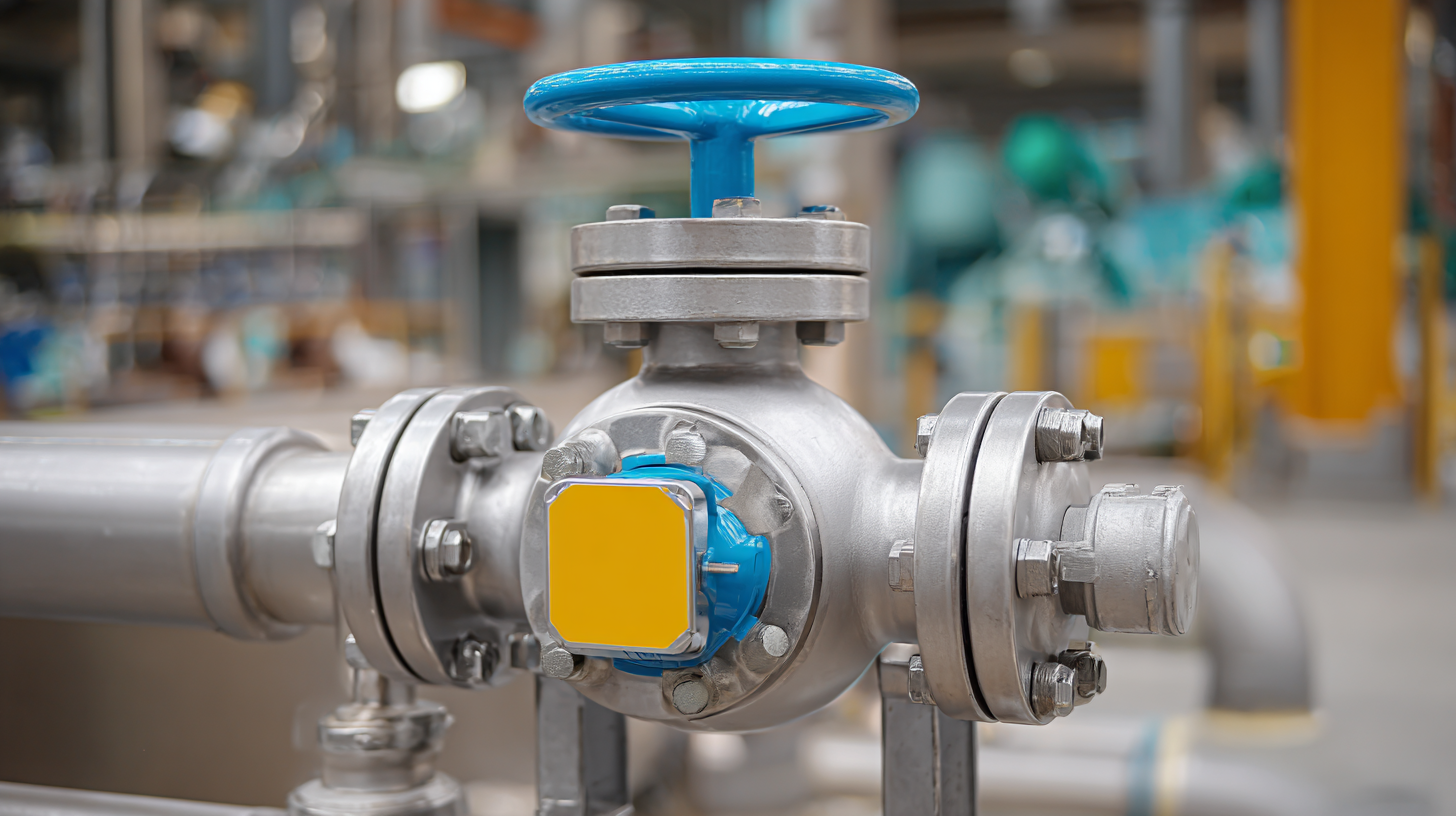

Choosing the right actuated ball valve for your industrial application involves several key factors that can significantly affect efficiency and operational reliability. First and foremost, it's essential to consider the valve's size and pressure rating. The valve must be adequately sized for the specific flow requirements of your system while also possessing the pressure rating necessary to handle the environment in which it will operate. Assessing flow rates and pressure drop can prevent potential issues and ensure optimal performance.
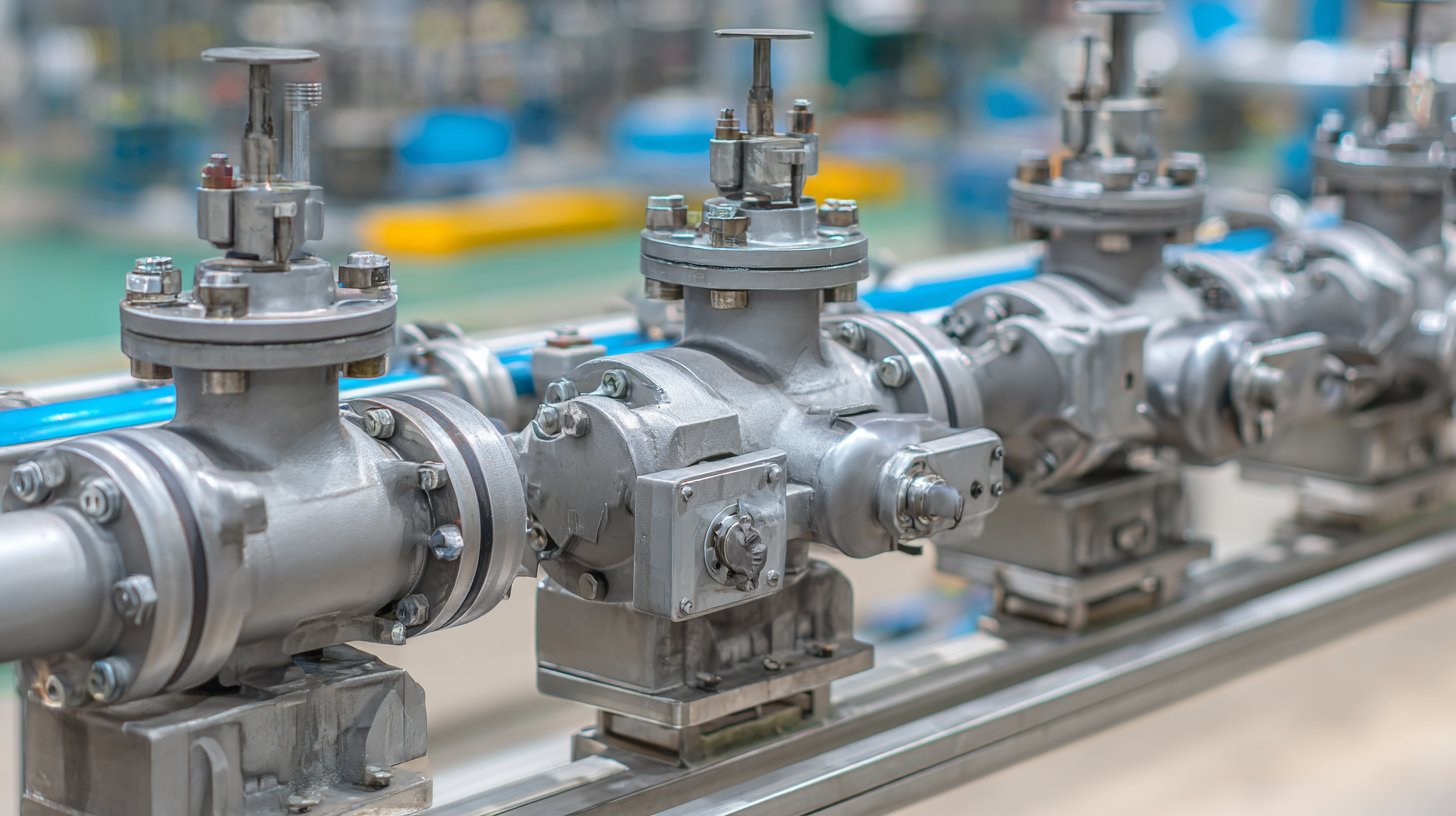
Another critical factor is the material composition of the valve. Depending on the fluids being handled—whether corrosive, abrasive, or at varying temperatures—selecting the appropriate material is vital for longevity and safety. For instance, a stainless steel ball valve might be ideal for corrosive substances, while plastic valves may be suitable for less aggressive applications. Additionally, the choice of actuator—whether electric, pneumatic, or hydraulic—should align with system requirements and constraints, such as available power sources and response times. These considerations ensure that the actuated ball valve you select will meet the specific demands of your industrial processes.
When selecting an actuated ball valve for industrial applications, understanding the different types of actuators is crucial. Actuators can be broadly classified into three categories: electric, pneumatic, and hydraulic. Each type offers unique advantages that cater to specific operational needs. Electric actuators are ideal for applications requiring precise control and automation, making them suitable for environments with consistent power supply. They generally provide easier integration with control systems, allowing for remote operation and monitoring.
Pneumatic actuators, on the other hand, are widely favored in environments where rapid response and high-speed operation are essential. They use compressed air to swiftly actuate the valve, making them an excellent choice for processes that demand frequent cycling. Additionally, pneumatic systems are often more reliable under harsh conditions, such as extreme temperatures or the presence of corrosive substances. Meanwhile, hydraulic actuators are best suited for applications that necessitate high torque and force, particularly in heavy-duty industries like oil and gas. Understanding the specific requirements of your application will guide you in selecting the right actuator type to enhance efficiency and reliability in your operations.
When selecting an actuated ball valve for your industrial application, assessing valve materials is crucial for ensuring both durability and performance. The materials used in ball valves play a vital role in their ability to withstand various operating conditions, including temperature extremes, corrosive substances, and high-pressure environments.
For instance, stainless steel is often favored for its resistance to corrosion and high strength, making it suitable for a wide range of industries, such as oil and gas or chemical processing. On the other hand, materials like PVC or CPVC may be appropriate for less demanding environments, offering a cost-effective solution while maintaining adequate performance.
In addition to the primary construction materials, it's important to consider the sealing components of the valve. Elastomers such as PTFE or nitrile rubber provide excellent sealing properties but vary in chemical compatibility and temperature resistance. Choosing the right sealing material is essential to prevent leaks and ensure the longevity of the valve. By carefully evaluating both the valve body and sealing materials, you can ensure optimal performance and durability tailored to your specific industrial needs, ultimately leading to enhanced operational efficiency and reduced maintenance costs.
When selecting actuated ball valves for industrial applications, making the right choice is crucial to ensure efficiency and longevity in operation. One common mistake is not fully understanding the specific requirements of your system. It is essential to consider the fluid type, pressure, temperature, and flow characteristics before making a decision. Neglecting these factors can lead to valve failure or inefficient operation, resulting in costly downtimes.
Another frequent oversight is underestimating the importance of actuator sizing and type. Ball valves require an appropriately sized actuator to function correctly; an undersized actuator may not provide sufficient force to open or close the valve, while an oversized one could cause unnecessary wear. Additionally, selecting the wrong actuator type—whether electric, pneumatic, or hydraulic—can severely impact performance. Thoroughly evaluating the operating environment and load requirements ensures the actuator chosen complements the valve, thereby maximizing reliability and performance.
| Criteria | Considerations | Common Mistakes |
|---|---|---|
| Application Type | Identifying whether the valve will be used for isolation, flow control, or throttling. | Not aligning valve type with application requirements. |
| Size Selection | Proper sizing based on flow rate, pressure, and pipe dimensions. | Choosing a valve that is too large or too small. |
| Material Compatibility | Selecting valve materials that resist corrosion and pressure from media. | Ignoring compatibility with the fluid being handled. |
| Actuation Method | Electric, pneumatic, or hydraulic actuators based on power availability and required speed. | Overlooking the advantages and limitations of each actuation method. |
| Pressure and Temperature Ratings | Ensure the valve can handle the maximum pressure and temperature of the system. | Selecting a valve without verifying its pressure and temperature ratings. |
| Maintenance Requirements | Assess the ease of maintenance and the availability of spare parts. | Ignoring the long-term maintenance needs of the selected valve. |





Accreditations
ISO 9001 Quality Management
HSE Management Compliant
Products and services comply with relevant Australian (AS) and international (ISO, etc.) Standards.
"*" indicates required fields